5 Factors That Increase the Risk of Melanoma
Melanoma or skin cancer is one of the less common forms of cancer that originates from melanocytes. It is also a very dangerous form of cancer that spreads rapidly to other organs if not treated in the early stages. Apart from knowing the symptoms to treat the disease, it is also equally important to know the following risk factors that increase the probability of getting diagnosed with melanoma.
1. Exposure to ultraviolet light
This is one of the major risk factors associated with melanoma. Ultraviolet light is found in abundance in sunlight, sunlamps, and tanning beds. There are specific areas that experience more exposure to UV rays. Exposure to these rays can alter skin genetics and even damage the DNA resulting in its mutation. The mutation causes the cell to grow out of control resulting in the formation of a malignant tumor. Evidence suggests that the body parts that are more prone to develop this form of cancer include the chest, back, and legs. People living in areas where UV radiation is higher than normal may stand a risk of developing this form of cancer on the face, neck, and arms. However, there are very rare cases where patients have developed mucosal melanoma on internal surfaces like the mouth and vagina where there is no sun exposure.
2. Fair skin
It is yet another one of the most common risk factors of melanoma. Fair skin is usually a sign of low levels of a pigment called melanin. People who experience burns or freckles and never tan when exposed to sunlight are more prone to suffer from skin cancer or melanoma. It has also been observed that people with blue or green eyes with red or blonde hair stand a greater risk of suffering from melanoma.
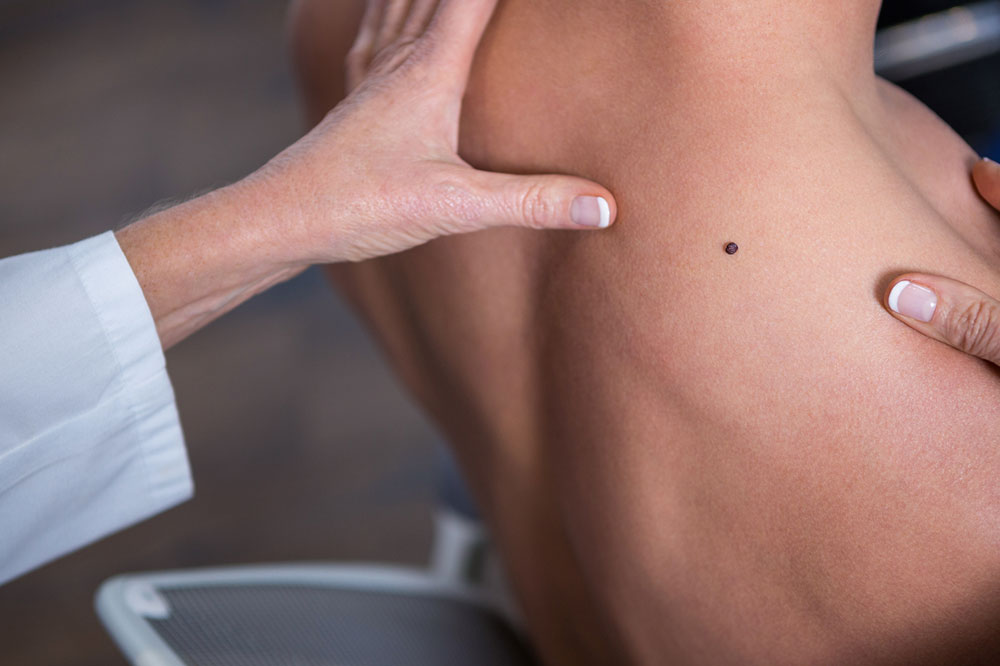
3. Moles
A higher number of moles on the body increases the chances of suffering melanoma. Moles are usually benign or non-cancerous and often appear in children and young adults. It has been observed that a larger size of moles may undergo mutation and turn cancerous. These moles do not have well-defined borders and have an uneven surface. Such moles are termed as dysplastic nevi or atypical moles, and they often appear on skin that is either overexposed to direct sunlight or usually covered most of the time. Apart from this, moles present since birth also have a chance of developing into cancer. These moles are called congenital nevi and are also sometimes removed by surgery to eliminate the possibility of turning into a cancerous tumor.
4. Family history
The risk of suffering from melanoma increases if first-degree relatives such as parents and siblings have a history or are currently suffering from melanoma. This could be because of a combination of factors such as sharing the same genetic abnormalities and lifestyle.
5. Weakened immune system
The immune system helps in fighting infections and keeps diseases at bay. However, a weakened immune system due to an underlying health condition or disease can also increase the risk of developing mutation in the melanocytes, thereby causing melanoma.


